Diabetic Retinopathy
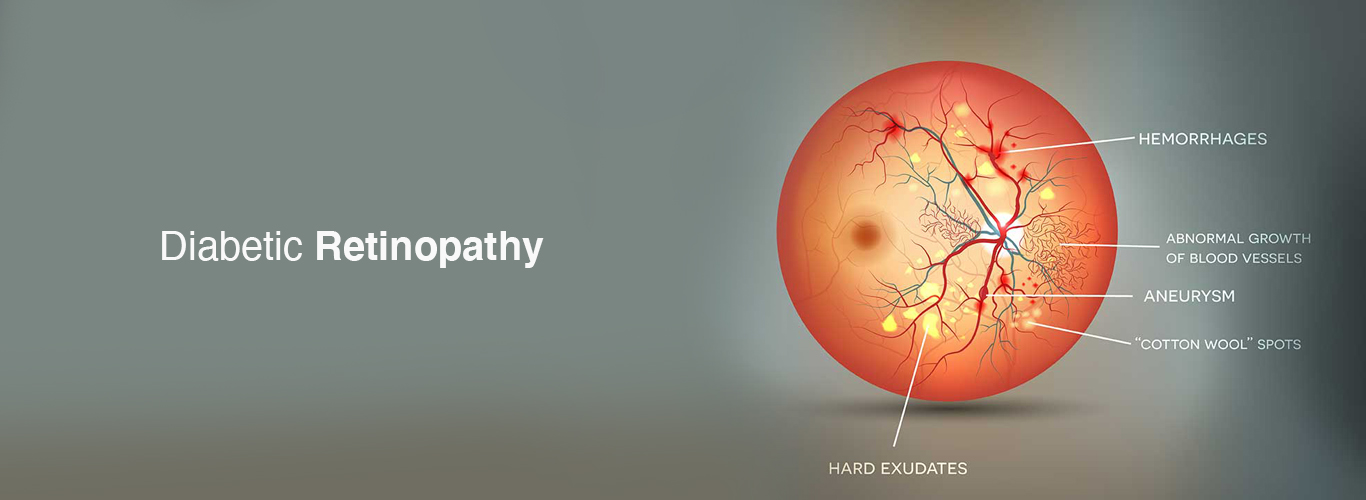
Diabetic Retinopathy is the leading cause of Blindness in the working age group population worldwide. The prevalence of diabetes is rising with increasing industrialization and globalization along with sedentary lifestyles. Consequently, the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy is also expected to increase especially with increased life expectancies. The duration of Diabetes is the major risk factor in the development of retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy is the ocular manifestation of end-organ damage in Diabetes. Retinal neurodegeneration followed by microvascular abnormalities result in retinal damage.
Only about 60% of people with diabetes are screened annually for diabetic retinopathy. There needs to be a lot more referrals to the Ophthalmologists for retinal screening.
People with type 1 diabetes should have annual screenings for diabetic retinopathy beginning 5 years after the onset of their disease, whereas those with type 2 diabetes should have a prompt screening at the time of diagnosis and mandatory yearly screenings thereafter. A dilated retinal examination along with retinal fundus photography for documentation is recommended. Patients with manifested diabetic retinopathy are monitored more frequently as required.
Women with diabetes who become pregnant should be monitored closely during their pregnancies because the disease can progress rapidly. However, an eye examination is not required when gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.
Maintaining blood sugar, blood pressure and serum lipid levels lowers the risk of retinopathy developing and/or progressing, so patients must be informed of the importance of maintaining good levels of glycosylated haemoglobin along with normal blood pressure and blood lipid levels. It is also vital to educate patients that during early stages of the disease, the vision remains normal. It is only during the moderate and late stages of the disease that visual impairment occurs.
Management options for diabetic retinopathy includes following a healthy diet and lifestyle, medical management, timely ophthalmic evaluation, and treatment under the care of an ophthalmologist. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections are effective in the treatment of diabetic macular oedema. Laser pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP) remains the mainstay treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Late stages may require vitreous surgery along with retinal endo laser at the time of surgery.
Early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy plays a pivotal role in optimizing treatment outcomes and preventing visual impairment or loss.
Discover crucial insights about diabetic retinopathy, a prevalent eye disease among individuals with diabetes, and a significant cause of blindness in adults. LLH Hospital’s ophthalmology specialists provide comprehensive information to help you understand and tackle this condition effectively. Stay informed and take control of your eye health with LLH Hospital’s expert guidance on diabetic retinopathy.